Finite State Machines in JavaScript
Finite State Machines in JavaScript
By Dave Bitter
4 min read
Application state can make any application complex real quick. Let’s have a look at Finite State Machines in Javascript to resolve some of these complexities.

- Authors

- Name
- Dave Bitter
Finite State Machines (FSMs) are a concept in programming that helps model complex systems with a fixed set of states and transitions between those states. In JavaScript, FSMs offer a structured approach to managing application logic for making code more organised, easier to maintain and more.
What is a Finite State Machine?
An FSM is a model that consists of three main components:
- States: the distinct stages or conditions an application can be in at any given moment
- Transitions: the description of how the FSM moves from one stage to the other
- Events: the triggers for a transition of state
Example of an FSM
Let’s have a look at an example to make this concept more practical. Imagine an e-commerce website that tracks the status of a user's order. The order can be in various states, such as "Pending", "Processing", "Shipped" and "Delivered". The system is designed without using an FSM, relying on complex nested if-else statements to handle state transitions:
let orderStatus = 'Pending'
const updateOrderStatus = (event) => {
if (orderStatus === 'Pending' && event === 'ProcessOrder') {
orderStatus = 'Processing'
} else if (orderStatus === 'Processing' && event === 'ShipOrder') {
orderStatus = 'Shipped'
} else if (orderStatus === 'Shipped' && event === 'DeliverOrder') {
orderStatus = 'Delivered'
} else {
console.log('Invalid state transition or event.')
}
}
Usually this is the moment I get a coffee to start figuring out what the business logic is in this function. As the codebase grows, more state transitions are added, leading to a convoluted and error-prone updateOrderStatus function. The lack of structure and clear separation between states and transitions make it challenging to maintain, debug, and extend the code.
By using an FSM, we can significantly improve the code's clarity and maintainability. Let's see how the same order status functionality can be implemented with an FSM:
const states = {
PENDING: 'Pending',
PROCESSING: 'Processing',
SHIPPED: 'Shipped',
DELIVERED: 'Delivered',
};
const transitions = {
ProcessOrder: {
[states.PENDING]: states.PROCESSING,
},
ShipOrder: {
[states.PROCESSING]: states.SHIPPED,
},
DeliverOrder: {
[states.SHIPPED]: states.DELIVERED,
},
};
let orderStatus = states.PENDING;
const function updateOrderStatus => (event) {
const nextState = transitions[event][orderStatus];
if (nextState) {
orderStatus = nextState;
} else {
console.log('Invalid state transition or event.');
}
}
With the FSM implementation, the code becomes more structured and organised. When calling the updateOrderStatus function with "ProcessOrder" event, the state can only go to "Processing" if the current state is "Pending". This is the same business logic as before, but states and transitions are clearly defined, making it easier to understand the system's behaviour.
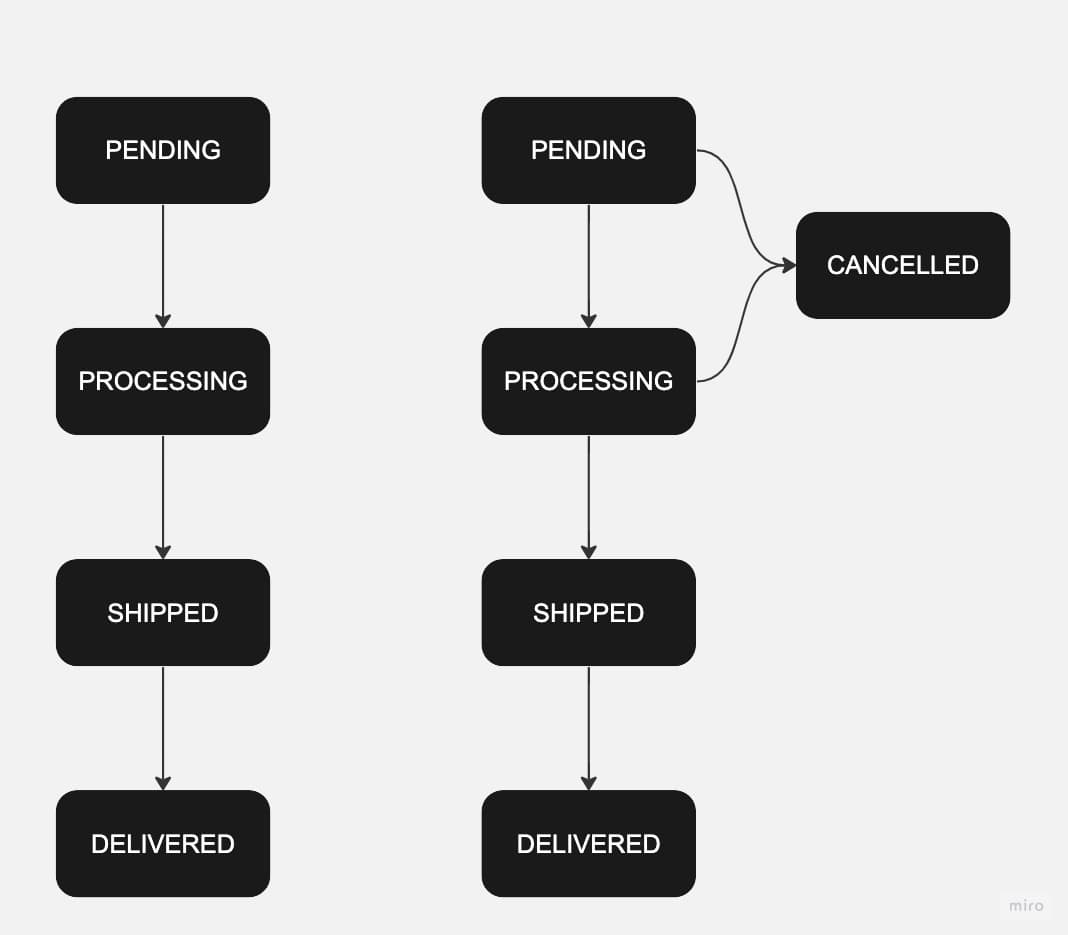
As the number of states and transitions increases, the code remains clean and maintainable. For example, if you want to add a cancelled order state, you simply update the states and transitions objects:
const states = {
PENDING: 'Pending',
PROCESSING: 'Processing',
SHIPPED: 'Shipped',
DELIVERED: 'Delivered',
CANCELLED: 'Cancelled',
};
const transitions = {
ProcessOrder: {
[states.PENDING]: states.PROCESSING,
},
ShipOrder: {
[states.PROCESSING]: states.SHIPPED,
},
DeliverOrder: {
[states.SHIPPED]: states.DELIVERED,
},
CancelOrder: {
[states.PENDING]: states.CANCELLED,
[states.PROCESSING]: states.CANCELLED,
}
};
let orderStatus = states.PENDING;
const function updateOrderStatus => (event) {
const nextState = transitions[event][orderStatus];
if (nextState) {
orderStatus = nextState;
} else {
console.log('Invalid state transition or event.');
}
}
As you might notice, for the CancelOrder transition the state can only be cancelled if the order was in the “Pending” or “Processing” state. Other wise the user can’t cancel and as there is no transition implemented and you can handle your logic accordingly.
Benefits of Using Finite State Machines in JavaScript:
- Clarity and Organization: FSMs provide a clear and organised representation of application logic. By breaking down complex behaviour into states and transitions, FSMs make the codebase more comprehensible and easier to follow. This clarity ensures that developers, both new and experienced, can understand the system's behaviour without diving into intricate details.
- Modularity and Reusability: FSMs encourage modularity by compartmentalising states and transitions. Each state represents a well-defined portion of functionality, making it easy to reuse and combine states across different parts of the application. This modular approach reduces code duplication and allows developers to build applications with more flexibility.
- Predictable Behavior: FSMs enable predictable behaviour in an application. Since each state and transition is explicitly defined, the system's responses to events become consistent and deterministic. Predictable behaviour is crucial for building robust and reliable applications, as it reduces the likelihood of unexpected bugs and unpredictable user experiences.
- Easy Debugging and Testing: With FSMs, debugging and testing become more straightforward. The structured representation of states and transitions simplifies the process of identifying potential issues and bugs. Additionally, writing test cases for FSMs becomes more manageable, as each state can be tested independently, verifying that the system behaves correctly in different scenarios.
- State Management: FSMs provide a systematic way to manage the application's state changes. As the system evolves, FSMs help developers maintain a clear overview of the states and their relationships. This structured state management contributes to better code maintainability, scalability, and overall code quality.
Finite State Machines offer a structured and organised approach to managing stateful behaviour in JavaScript applications. The benefits of FSMs, including clarity, modularity, predictability, easy debugging, and better state management, make them a valuable tool for simplifying complex systems and enhancing code quality. By embracing Finite State Machines, developers can avoid the issues that arise from poorly managed application logic and build more robust and maintainable JavaScript applications.