WebAuthn: it's time to forget your passwords
WebAuthn: it's time to forget your passwords
By Jelle Biesemans
4 min read
Dive into the browser standard of securing login and authentication using the WebAuthn browser API

- Authors

- Name
- Jelle Biesemans
WebAuthn: it's time to forget your passwords
Imagine a world where the hassle of remembering and resetting passwords is a thing of the past. In this article, we'll dive into WebAuthn, a web standard that eliminates passwords, replacing them with a more secure and convenient login experience.
With WebAuthn, accessing your favorite websites becomes effortless, allowing you to focus on what truly matters. Step into a future where authentication is seamless and secure, liberating you from the burden of passwords.
What is WebAuthn
Since March 2019, the W3C announced that WebAuthn is the official web standard for password-free login.
It is a browser-based API that allows web applications to simplify and secure user authentication. This is done by using registered devices (such as phones and laptops) or biometrics (such as fingerprints) as factors. WebAuthn uses public key cryptography to protect users from advanced phishing attacks.
Why do the current methods fail us?
Usernames and passwords
We're all familiar with the original way of authentication: using usernames and passwords. Although this system is easy to understand for the common users, it certainly has its flaws.
Credentials are easily forgotten, people would write down their password somewhere if they didn't use a password manager, ...
It was found that this way of authentication was not the safest way and the need for a more secure authentication system rose.
2FA
An extra authentication step was introduced with two-factor authentication (2FA). This extra step makes it harder for people with malicious intent to steal your password data and take over your accounts.
However, popular, low-assurance second factors like SMS and email are vulnerable to phishing attacks.
Benefits of using WebAuthn
Now, some benefits will be addressed. These will be split up by customers (web application users), product owners, and security teams (web application owners).
Let's see how WebAuthn provides both parties with its benefits.
Web-application users
WebAuthn completely removes the need for passwords. For users, this means not having to remember their login credentials, or requesting an OTP (one-time password) when using that as a second factor. The authentication flow is simplified to just use the registered device.
Customers are giving you their information. They want to know their data is safe when they share it. WebAuthn subverts associated with passwords and therefore is a much more secure authentication method.
Web-application owners
Product owners care about the use of their applications, and removing customer-facing barriers, such as complex authentication, is one of their highest priorities. WebAuthn contributes to a better login experience.
Security teams need to be less involved. Since the private key never leaves the user's device, the risk of spoofing authentication is lower. The only way to get access to an account is by physically stealing the registered device.
How does it work?
So when WebAuthn removes the need for actual passwords, how does it go about authenticating the user? How does it do the things it is doing?
WebAuthn has three main components that make all the magic happen:
- the authenticator
- the browser
- and the web server
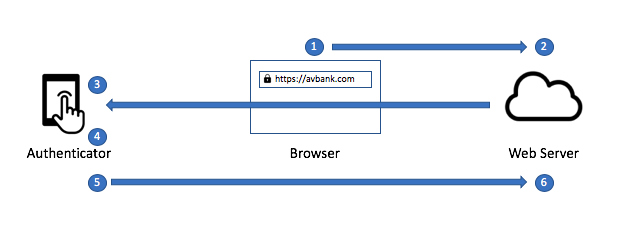
Authentication process
Using those three components, the authentication process can be explained as follows:
- The user goes to the browser to initiate the login
- The web server receives this login request, then creates a unique challenge and sends it to the authenticator
- The authenticator receives this challenge, including the domain name for the challenge
- The Authenticator receives biometric consent/passkey from the user
- The Authenticator generates a cryptographic signature (public-private keypair) which is sent back to the web server
- The web server verifies the signature to the unique challenge and logs the user in when verified
More information about the technical specs can be found here
Drawbacks
I can already hear you think: "WebAuthn, okay, all nice. But what if I lose my device on which my private key is stored?"
The answer is simple: you will be locked out of your account, with no way to recover it.
That is why it is important to have some fallbacks. Here are some ways that might just prevent you from getting locked out of your account:
- register multiple devices
- use a password manager like 1Password to store your private key (this can also be used with multiple devices)
Browser support?
WebAuthn is supported in all major browsers, except for
- Firefox: partial support because TouchID is not yet being supported.
Some smaller browsers
- Firefox for Android: not supported when a PIN is set
- Opera mini: no support at all
- IE: no support at all, but it's IE after all 🙈
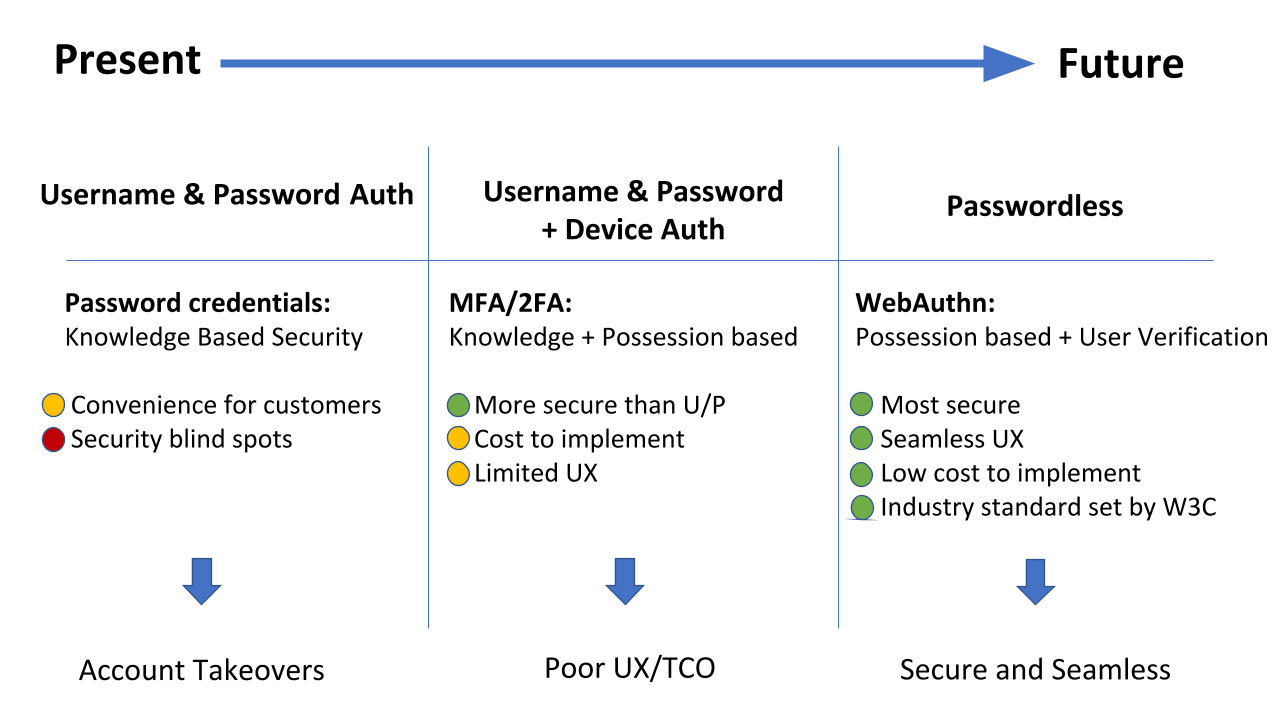
What does the future bring?
Authentication is shifting more and more towards passwordless. Accounts will be more secure and the risk of account takeovers and limited user experience will be problems of the past.
That's why it is time to forget about your passwords and start using passwordless logins!
Useful links
- https://www.okta.com/blog/2019/03/what-is-webauthn/
- https://dev.to/dagnelies/webauthn-what-if-i-loose-my-device-1lbh
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Authentication_API
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Credential_Management_API